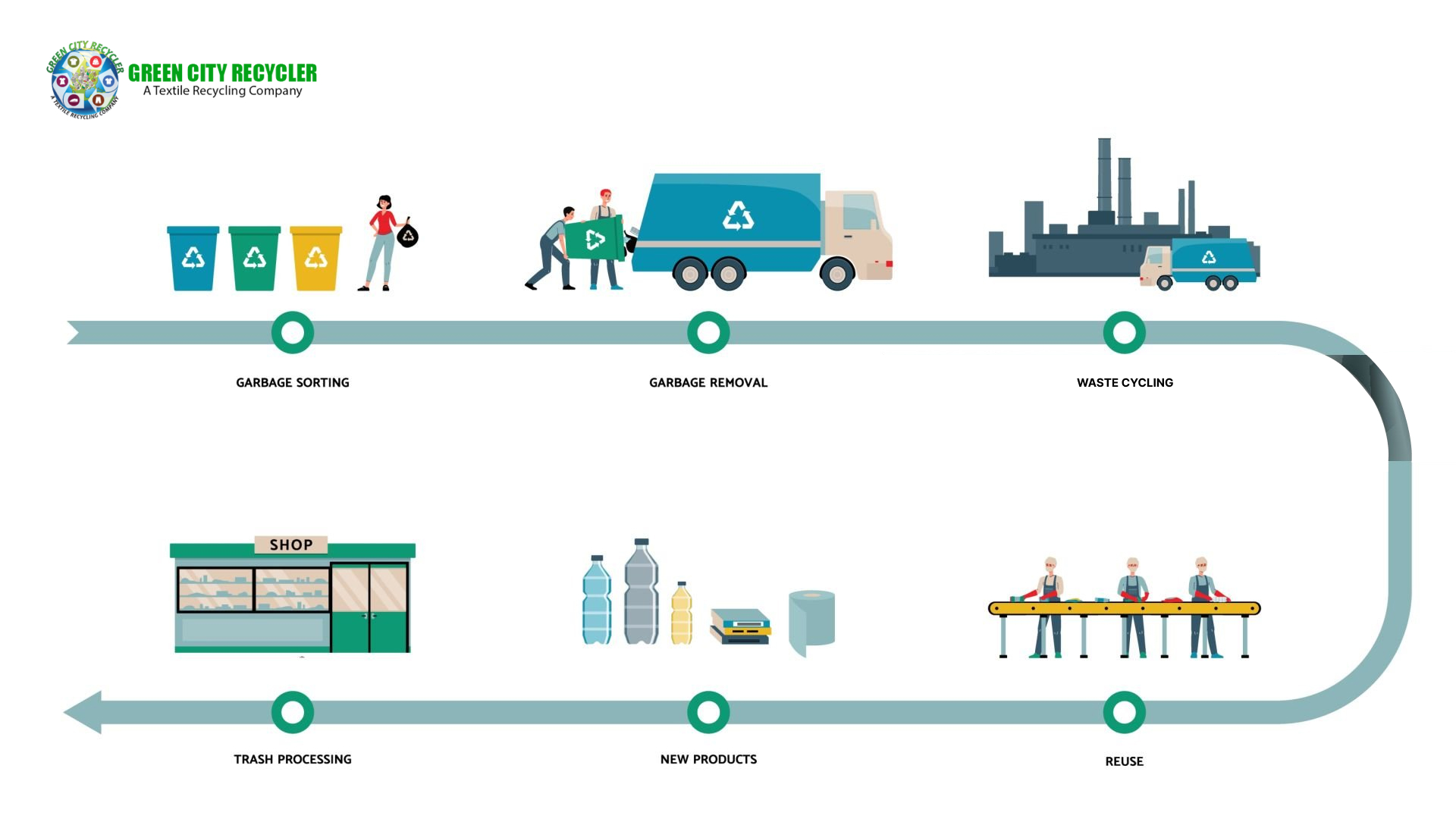
From food and furniture to clothes and technology, the building components of the goods we use daily are raw materials. Still, these materials go through several processing phases before they are finalized goods. Knowing this process enables us to value the things we consume and emphasizes how manufacturing affects the surroundings. This blog streamlines the procedures required in handling common how are the raw materials processed including synthetics, metals, and natural resources.
1. Describe raw materials
Raw materials are semi-processed or natural compounds utilized in the roofing based manufacturing of completed goods. Three main categories can help one to classify them:
- Natural raw materials, like wood, cotton, and oil, are gathered straight from the earth.
- Extracted from the ground, minerals and metals include aluminum, gold, and iron ore.
- Designed from chemical processes, synthetic materials include plastics and synthetic fibers.
- Every kind of raw material goes through particular processes to become something someone might use.
2. Processing Raw Materials: Steps
Usually, raw material processing consists of three primary phases:
- Extraction: Getting the raw good from its source.
- Refining the material means either cleaning or separating it to render it usable.
- Conversion: Turning it into a component or workable good.
- Let us explore how these processes apply to several basic materials.
3. Handling Original Raw Materials
Wood
Building, furniture, and paper manufacture all need wood. The scheme begins with:
- Usually known as logging, trees are taken down in carefully designated places.
- Logs are driven to mills where they are:
- For furniture or buildings, sawn into boards.
- Pulped to make paper.
- Dried and treated planks help to avoid decay and bugs. Paper pulp is turned into sheets.
- Reforestation and exploiting every aspect of trees help minimize environmental effects and waste through sustainable methods.
Cotton
Natural fibers typically utilized in textiles are cotton. The procedure consists in:
- Harvesting cotton from plants either by hand or by machine.
- Machines ginning cotton fibers remove seeds and trash from them.
- Fibers are spun into yarn.
- Yarn is spun into fabric, then dyed and completed for use in clothes or other goods by knitting or weaving.
- Modern techniques seek to cut pesticide and water use during cotton growing.
4. Managing Metals and Minerals
Transportation, technology, and building all depend on metals in a great part of how are the raw materials processed. Their processing takes multiple phases:
Iron and Steel Mining
Iron ore comes from the ground.
- Ore is broken down into tiny bits via crushing and grinding.
- To extract iron, ore is burned in a blast furnace using coke—a carbon-rich substance.
- Refining removes contaminants to create pure iron or steel.
- Shaping: The metal is formed into either specified components, bars, or sheets.
Aluminum Mining:
Extracted is bauxite, the main supply of aluminum.
- Separating aluminum oxide from the bauxite, the Bayer process refines:
- Pure aluminum is extracted from the oxide by electrolysis—that is, with electricity.
- Aluminum is formed either shaped into goods or into sheets.
- Among the most recyclable metals, aluminum helps to save resources and energy.
Gold Mining
Gold comes from riverbeds or mines.
- Ore is broken down into free gold particles.
- Gold is extracted chemically either from other elements using cyanide or mercury.
- Gold is refined to reach the necessary purity for coinage, electronics, or jewelry.
5. Working with Synthetic Materials
Plastic and nylon are synthetic materials created man-made by chemical processes.
Plastics Raw materials
Natural gas or petroleum fuels plastics’ manufacture.
- Chemical reactions transform basic materials into polymers—chains of molecules—in polymerization.
- Melted polymers are formed into goods by extrusion or molding.
- Products are finished for packaging by means of cooling.
Synthetic fibers, like polyester
- Polymer fibers are produced from petroleum-based compounds by chemical synthesis.
- Spinning fibers result in threads or yarns.
- Fabrics are made from threads.
- Fabrics are treated for durability and dyed and finished.
- Synthetic materials are being recycled, and reliance on fossil fuels is being lessened efforts aim at.
6. Environmental Effects of Processing Raw Materials
Although how are the raw materials processed is crucial, it usually costs the environment:
- Deforestation: Climate change and habitat loss can follow from wood exploitation.
- Harmful chemicals released by metal mining and processing contaminate air and water.
- Making synthetic materials calls for large amounts of energy, generally derived from non-renewable sources.
- Processing sometimes generates byproducts that could damage ecosystems.
Industries are implementing environmentally friendly policies, such as recycling, employing renewable energy, and using waste-minimizing techniques, to help offset these effects.
7. Ecological Methods of Raw Material Handling
Here are ways both businesses and people may help sustainability:
- Encourage the usage of recycled goods like plastics, paper, and metal.
- Effective technology: Use cutting-edge equipment that lowers energy use and waste generation.
- Environmental source: Choose environmentally friendly materials like organic cotton or FSC-certified wood.
- Back environmentally friendly businesses: Select companies whose values center on ethical and environmentally friendly behavior.
8. Why Raw Material Processing Matters
Understanding the processing methods of raw materials guides our decisions as consumers. As an illustration:
- You might choose goods manufactured from recycled metals.
- Select biodegradable materials above polymers.
- Back businesses that run their operations on green energy.
- Every decision we make will help to improve sustainability and lessen the effects of raw material processing on the surroundings.
From Raw to Ready: Conclusion
It is interesting to see how are raw materials processed, turning natural resources into the daily items we need. From the cotton in our clothes to the metal in our devices to the wood in our furniture, every element goes through several processes to become useful and efficient.
There is an environmental cost associated with this metamorphosis, though. Understanding the procedures and selecting sustainable solutions will help us promote environmentally friendly behavior and lessen the negative effects of manufacturing. Let us value the resources around us and work for a time when their processing respects the earth.
Why Choose Green City Recycler for Raw Material Processing?
Emphasizing sustainability and environmental responsibility, Green City Recycler is a respected leader in recycling and repurposing raw materials. Their creative processing techniques guarantee that other items, including textiles, are diverted from landfills and turned into valuable commodities.
Working with Green City Recycler helps you help to lower waste, preserve natural resources, and advance a circular economy. Raw material recycling and processing depend on them because of their open procedures, community-driven projects, and dedication to environmentally friendly methods. Selecting Green City Recycler supports sustainable raw material management and helps us move toward a cleaner future.